
With the cost of living still high in many parts of Canada and average credit card interest rates hovering around 21%, managing day-to-day finances has never been more important. While credit cards are often associated with debt, when used wisely, they can be a powerful tool for improving your cash flow, earning rewards, and keeping your financial life organized. But be warned: If misused, that powerful piece of plastic can quickly turn into an debt anchor as it sinks your budget.
To help, here’s a primer on how to use credit cards to your advantage. In particular, learn how to track spending, time payments, and make the most of features like grace periods and cash-back programs. With a bit of discipline and the right tools, you can turn a credit card into the cornerstone of smart money management.
Learn More: Cut down debt faster with a simple 2-step plan
Treat yourself like a business
Before we bring credit cards into the picture, let’s start with a very simplistic financial mindset to get you on the right foot: think of your own life as you would a business. A restaurant will quickly go under if it spends more to pay staff, rent, and buy ingredients than it earns from the sale of prepared food. An individual’s bank account must be given the same consideration.
This idea manifests itself in a strategy that looks simple on paper, but can be difficult in practice: spend less than you earn. To help enforce self-imposed limits and act responsibly, it’s recommended to create a personal cash flow statement that accounts for all monthly income and spending.
Track income and expenses with care
You might be surprised by how many small, irregular purchases crop up when you keep perfect track of your spending. Every expended cent should be recorded, as they can otherwise accumulate over time and leave mysterious, unexplained gaps in a cash flow chart. Incoming cash, while usually more predictable, also needs to be correctly documented. Ensure that your cash flow statement includes the following entries:
- Regular Income: This includes your steady income and spousal income if applicable. The easiest to record is salary, but bonuses and commissions should also be listed. Do not include reinvested or locked income such as dividends, or unrealized gains from equity investments that are still open, for example. This money isn’t liquid, so it isn’t immediately relevant for the purposes of modeling your incoming cash.
- Peripheral Income: Other, typically smaller sources of cash can be placed in this section, which might include consulting or freelancing income, government benefits, pensions, dividends and investment residuals that aren’t steady enough to be included in the ‘Regular Income’ section.
- Fixed Expenses: Predictable expenses should be entered in the correct amount and date they’re expected to be paid, and might include things like mortgage and lease payments, rent, taxes, and scheduled investment contributions. However, as many shoppers can attest to, the list doesn’t end here.
- Variable Expenses: The most troublesome part of any cash flow statement, variable income consists of the bills that are largely circumstantial in nature. They can be hard to predict, and prove even harder to track. Purchases like groceries, clothes, entertainment expenses (restaurants, movies, streaming subscriptions, etc.), medical care and ATM withdrawals go here.
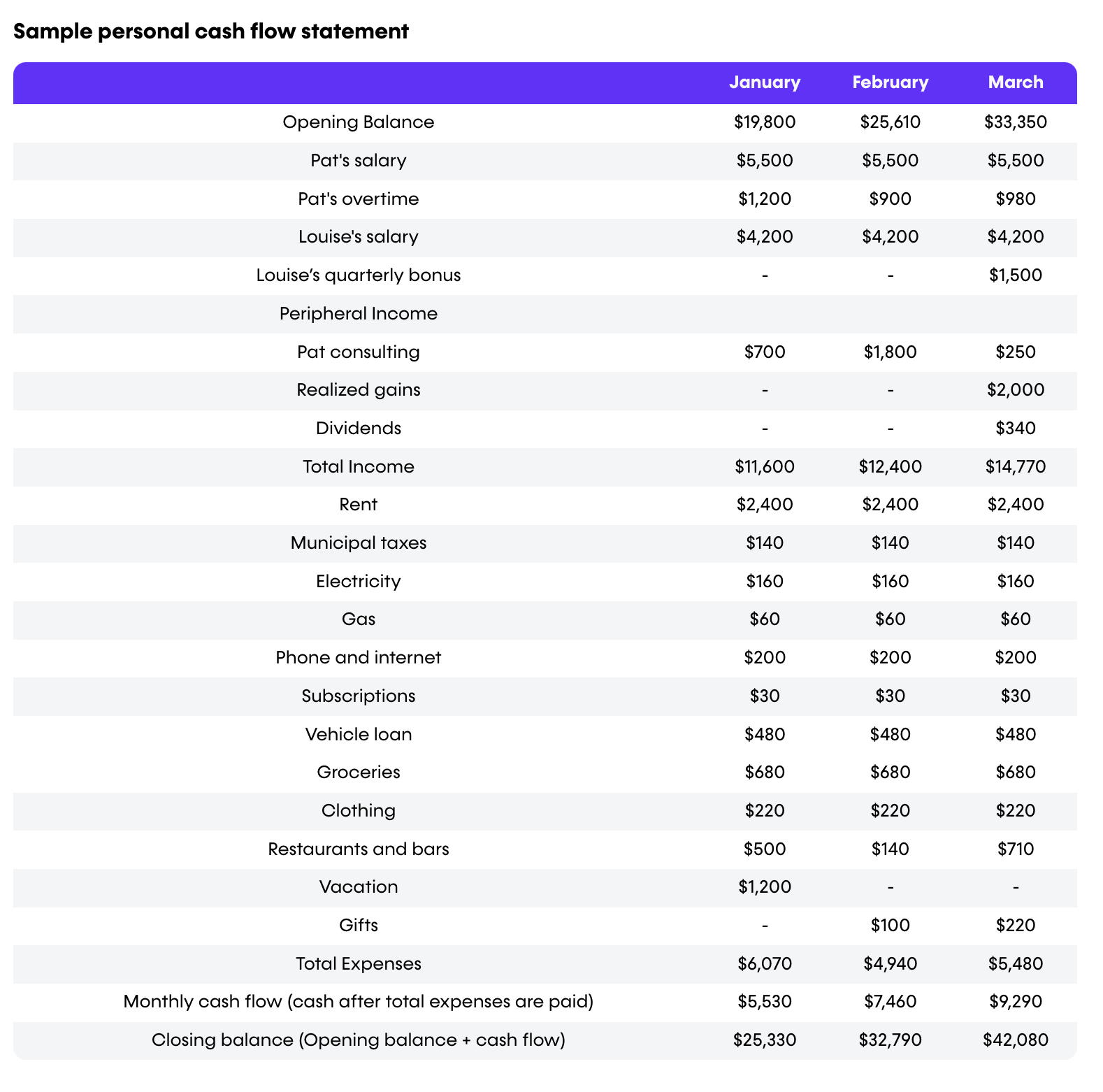
Sample personal cash flow statement
Below, you can see how fictional couple Pat and Louis keep track of their monthly incomes and expenses. By living below their means and practicing diligent financial upkeep, the couple is able to land in the black each month.
Maintain a documented record of purchases
Your first go at maintaining a cash flow chart might be challenging. It takes time and practice to make something a habit, and most individuals don’t have the discipline required to save hard copies of all their receipts. This means that a lot of purchases made in cash can potentially fall through the cracks rather than find their way onto a cash flow chart.
Using credit cards instead of cash helps preserve a more thorough record of purchases (though it’s still recommended to save receipts as a backup). And aside from making it easier to track expenditures, the use of credit cards can also earn rewards points that can help you reduce travel costs, or generate cash back directly from various expenses.
Pay bills on time
Delinquent bills accrue interest and fees, which can slowly send manageable debt into unmanageable territory. Using a credit card automates the process of paying bills, which has several advantages over paying them manually. The most significant advantage of automated bill pay is that you no longer need to rely on your memory, reducing the chance that you’ll miss a payment and incur a financial penalty. Automatic bill payments can often be customized, so that they only come due once the cardholder has already been paid their salary, for instance.
Many cards, like the Tangerine Money-Back Credit Card also offer incentives for scheduling automated payments and recurring bills that can make this cash flow management system especially attractive. But it pays to be careful. In 2023, the Canadian Anti-Fraud Centre reported over $530 million in losses from fraud, much of it tied to automated and recurring transactions. Always monitor your card statements even with automated payments enabled.
Moreover, credit cards grant users a grace period between when a statement arrives and when it must be paid. This basically amounts to an interest-free loan, as you’re purchasing something on credit without the requirement to pay for it immediately. Assuming the bill is paid within the grace period, no extra interest or fees on the purchase are added. The minimum grace period for many Canadian credit cards is 21 days, as per the Financial Consumer Agency of Canada; however, some card issuers may offer longer grace periods, and some issuers allow cardholders to set their preferred billing date. Not all credit cards will offer this flexibility, so before settling on a card it’s wise to compare the best credit cards for cash flow management.
Never carry a balance
It might be tempting to only pay the minimum balance and carry extra debt from month to month but it’s never recommended, particularly when the average credit card interest rate reaches more than 20%. In 2025, the average interest rate on a Canadian credit card was 20.99% — making it very costly to carry a balance. Those who tend to overspend should remember that interest effectively adds to the purchase price of an item and this cost compounds when it takes longer to pay off the balance.
Chronic overspenders might consider reducing their credit limits, which diminishes the ability to indulge and reduces the chance of having to carry a balance that can’t be paid off each month. But be warned that a reduced credit limit might also have a negative impact on credit utilization ratio — a metric that’s very relevant to good credit scores.
Taming the cash flow beast
Since 2022, Canadians have experienced persistent inflation — particularly on groceries, transportation, and rent. According to the Bank of Canada, core inflation remained above 3% throughout 2024, reinforcing the need for diligent cash flow and credit card use.
Maintaining cash flow requires practice and discipline. But it’s worth the effort, as it results in significant savings over time if you stick to the plan and adjust accordingly for changes. With the proper tools in hand, being consistent is simple and exceptionally rewarding.
This article provides information only and should not be construed as advice. It is provided without warranty of any kind.